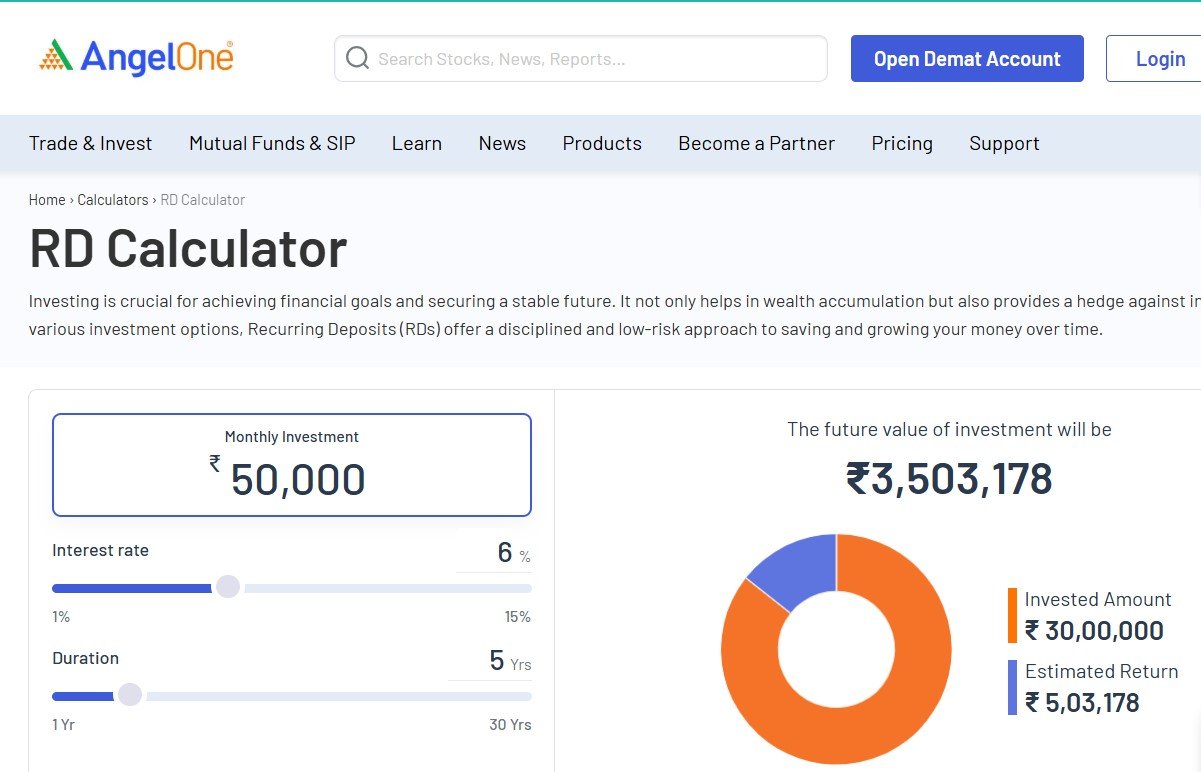
In today’s fast-paced and highly competitive business environment, logistics and supply chain management play a critical role in determining an organization’s success. From sourcing raw materials to delivering finished products to customers, a well-structured supply chain ensures smooth operations, reduced costs, and enhanced customer satisfaction. As global markets expand and customer expectations rise, businesses that invest in efficient logistics and supply chain management gain a significant competitive advantage.
Understanding Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Logistics and supply chain management (LSCM) refers to the planning, implementation, and control of the movement and storage of goods, services, and information across the entire supply chain. While logistics focuses on transportation, warehousing, inventory, and distribution, supply chain management takes a broader view by coordinating suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers.
Together, they form an integrated system that ensures the right products reach the right place at the right time and at the right cost. Effective logistics and supply chain management align operational processes with business objectives, enabling organizations to respond quickly to market changes.
The Importance of Efficient Supply Chain Operations
Efficiency is at the heart of successful logistics and supply chain management. Inefficient processes lead to delays, higher operational costs, excess inventory, and dissatisfied customers. On the other hand, optimized supply chain operations improve productivity, reduce waste, and enhance overall business performance.
Companies with efficient supply chains can manage demand fluctuations, minimize transportation costs, and maintain optimal inventory levels. This efficiency not only improves profit margins but also strengthens brand reputation and customer trust.
Key Components of Logistics and Supply Chain Management
1. Procurement and Supplier Management
Strategic sourcing and strong supplier relationships are essential for maintaining consistent quality and cost control. Businesses must evaluate suppliers based on reliability, pricing, and delivery performance to ensure uninterrupted supply.
2. Transportation Management
Transportation is one of the most significant cost factors in logistics. Optimizing routes, selecting reliable carriers, and using multimodal transport solutions help reduce transit time and expenses while ensuring timely deliveries.
3. Warehousing and Inventory Control
Efficient warehousing ensures proper storage, handling, and movement of goods. Advanced inventory management techniques, such as just-in-time (JIT) and demand forecasting, help reduce holding costs and prevent stockouts.
4. Distribution and Order Fulfillment
Seamless order fulfillment is critical for meeting customer expectations. Streamlined distribution networks and automated fulfillment processes ensure faster delivery and improved customer satisfaction.
Technology’s Role in Modern Logistics
Digital transformation has reshaped logistics and supply chain management. Technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, and cloud-based platforms provide real-time visibility and data-driven insights.
AI-powered analytics help forecast demand accurately, while IoT devices track shipments in real time. Warehouse management systems (WMS) and transportation management systems (TMS) automate processes, reduce human errors, and improve decision-making. These innovations enable businesses to operate smarter, faster, and more efficiently.
Driving Business Growth Through Supply Chain Optimization
An optimized supply chain directly contributes to business growth. By reducing operational inefficiencies, companies can lower costs and reallocate resources toward innovation and expansion. Faster delivery times and consistent product availability enhance customer loyalty and retention.
Moreover, scalable logistics and supply chain management systems allow businesses to expand into new markets with confidence. Whether entering international markets or launching new product lines, a robust supply chain ensures sustainable growth.
Sustainability in Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Sustainability has become a major focus for modern businesses. Environmentally responsible logistics practices not only reduce carbon footprints but also improve brand image and compliance with regulations.
Green logistics initiatives such as route optimization, fuel-efficient transportation, eco-friendly packaging, and sustainable warehousing help organizations minimize environmental impact. Integrating sustainability into supply chain strategies supports long-term growth while meeting social and environmental responsibilities.
Risk Management and Supply Chain Resilience
Global disruptions such as pandemics, geopolitical tensions, and natural disasters have highlighted the importance of resilient supply chains. Effective risk management strategies help businesses anticipate, mitigate, and recover from disruptions.
Diversifying suppliers, maintaining safety stock, and using predictive analytics enable organizations to build flexible and resilient supply chains. Strong logistics and supply chain management ensure business continuity even in uncertain conditions.
Customer-Centric Supply Chain Strategies
Modern supply chains are increasingly customer-centric. Today’s customers expect fast delivery, real-time tracking, and seamless returns. Businesses must design logistics strategies that prioritize customer experience.
By leveraging data analytics and automation, companies can personalize delivery options, improve order accuracy, and enhance transparency. A customer-focused supply chain not only boosts satisfaction but also drives repeat business and long-term growth.
The Future of Logistics and Supply Chain Management
The future of logistics and supply chain management is driven by innovation, automation, and collaboration. Emerging technologies such as autonomous vehicles, drones, robotics, and digital twins will further transform supply chain operations.
Additionally, data integration and end-to-end visibility will enable smarter decision-making. Businesses that embrace these advancements and continuously adapt their logistics strategies will stay ahead in an increasingly complex global market.
Conclusion
Logistics and supply chain management are no longer just operational functions—they are strategic drivers of efficiency and growth. By optimizing transportation, warehousing, inventory, and distribution, businesses can reduce costs, improve customer satisfaction, and achieve sustainable growth.
In a rapidly evolving business landscape, investing in advanced logistics and supply chain management solutions is essential for staying competitive. Organizations that prioritize efficiency, technology, sustainability, and resilience will not only meet today’s challenges but also unlock new opportunities for future success.