In today’s world of interconnected applications, smooth communication between systems is no longer optional—it’s essential. Whether you’re building an e-commerce backend, connecting a mobile app to a server, or integrating third-party services, REST APIs play a central role. For beginners stepping into java backend development, understanding how REST APIs work is one of the most important skills you can build.
Java has remained a dominant language in backend engineering due to its stability, scalability, and vast ecosystem of frameworks. Frameworks like Spring Boot make building RESTful services not just easier, but faster and more efficient. This guide breaks down what REST APIs are, how they work in Java, and why they’re indispensable for anyone getting started in java backend development.
What Is a REST API?
A REST API (Representational State Transfer API) is a set of rules that allows two software systems to communicate over HTTP. Instead of relying on complex protocols, REST uses simple web standards and allows data to be exchanged in lightweight formats like JSON.
REST architecture is built around a few core principles:
Stateless Communication: Each API call is independent. The server doesn’t store client session information.
Uniform Interface: Resources are accessed using clear, consistent URLs.
Client–Server Separation: Frontend/UI and backend logic remain separate.
Use of Standard HTTP Methods: GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.
For businesses and developers, REST APIs offer faster performance, easy scaling, and a clean structure that’s ideal for modern applications.
Why Java for REST API Development?
When people think of backend technologies, Java is usually among the top choices—and for good reason. Its robustness and ability to handle large-scale enterprise workloads make it a favorite.
Here’s why Java is perfect for building RESTful APIs:
Strong ecosystem with frameworks like Spring, Spring Boot, Jakarta EE.
High security, suitable for banking, fintech, and enterprise apps.
Cross-platform capability thanks to the JVM.
Excellent performance with multithreading and optimized memory use.
Active community support with continuous improvements.
Anyone who aims to grow in java backend development must understand how REST API frameworks fit into the bigger backend architecture.
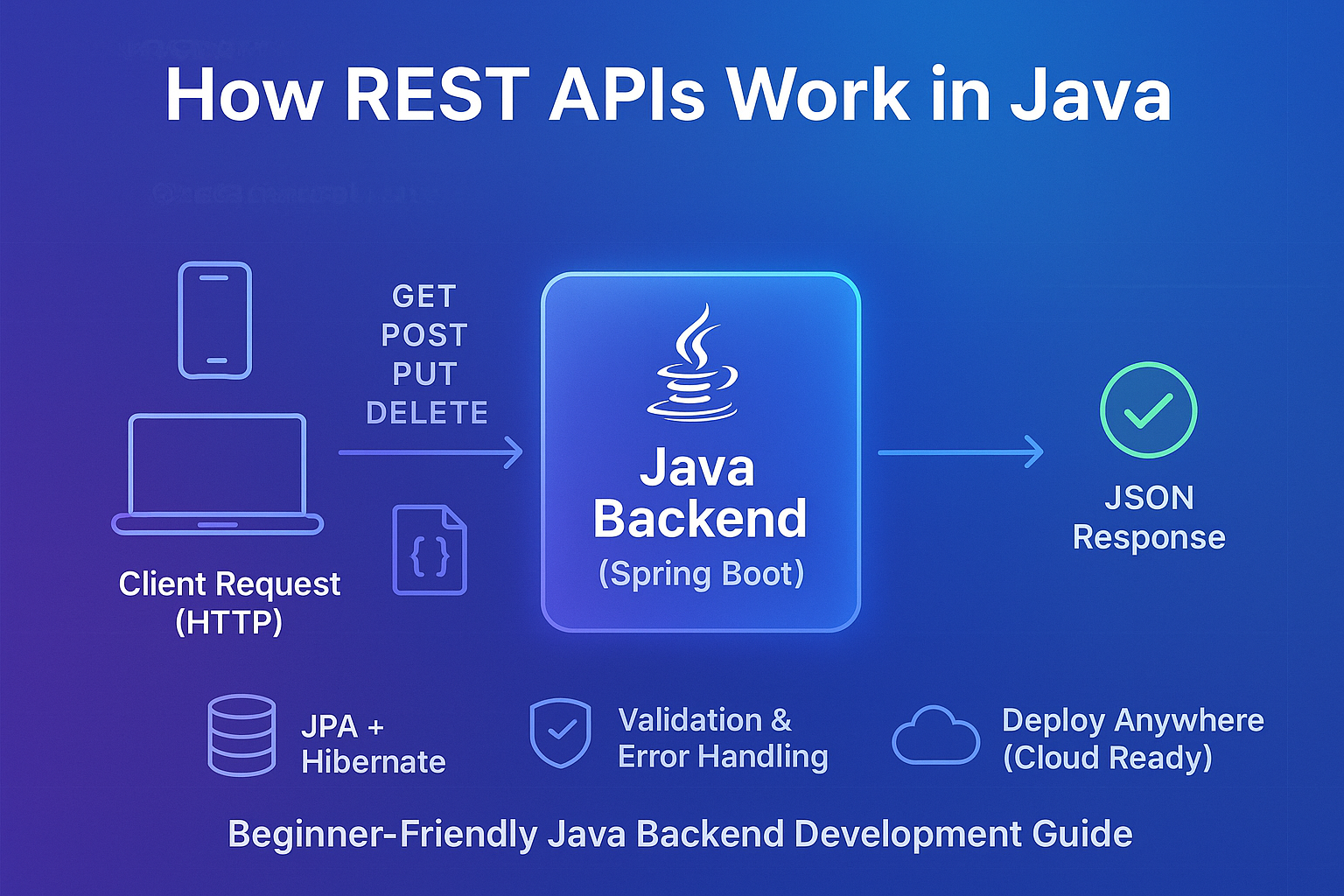
How REST APIs Work in Java
The most widely used combination for building REST APIs in Java is Spring Boot, a powerful framework that simplifies configuration and setup. It allows developers to create production-ready REST services with minimal boilerplate.
Let’s break down how REST APIs function in Java through the key components involved:
1. Controllers – Defining Endpoints
In Java, REST endpoints are typically created using @RestController and @RequestMapping annotations. A controller tells the application which URLs correspond to which backend logic.
Each method inside a controller represents an API endpoint. For example:
/users might fetch all users.
/users/{id} might fetch a single user.
/orders might create a new order.
This structure makes the application clean, modular, and easy to maintain.
2. HTTP Methods – Communicating with the Server
REST APIs heavily rely on standard HTTP methods:
GET – Fetch data
POST – Create data
PUT – Update data
DELETE – Remove data
Java’s Spring Boot maps these methods using annotations like @GetMapping, @PostMapping, etc. This clear mapping ensures that both developers and clients understand how each route should be used.
3. JSON – The Language of REST APIs
REST APIs usually send and receive data in JSON format. Java handles JSON using libraries such as Jackson, which automatically converts Java objects into JSON and vice versa.
This automatic data conversion is key in java backend development, helping developers focus on business logic instead of manual parsing.
4. Services – Managing Business Logic
While controllers handle incoming requests, the service layer manages the actual application logic. This ensures clean architecture:
Controllers → Handle request
Services → Process data
Repositories → Interact with database
This separation makes the application scalable and testable.
5. Database Integration – Storing and Retrieving Data
Backend APIs almost always interact with a database. Java commonly uses JPA (Java Persistence API) with Hibernate for ORM mapping.
Developers define entities, and Spring Data JPA handles the rest—making database operations easier, faster, and cleaner.
6. Error Handling & Validation
A good API must handle errors gracefully. Spring provides powerful exception-handling annotations to return meaningful responses:
400 for bad requests
404 for resource not found
500 for internal server error
Validation ensures clients send correct data, improving overall reliability.
Benefits of Learning REST APIs in Java
If you’re aiming for a career in java backend development, mastering REST APIs unlocks multiple opportunities:
Build scalable enterprise applications
Develop microservices-based architectures
Integrate mobile and web applications
Work with cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and GCP
Create secure, production-ready applications
REST APIs are the backbone of nearly every backend system, making them essential in the modern tech landscape.
Conclusion
Understanding how REST APIs work in Java is one of the most valuable skills for developers stepping into backend engineering. Java’s strong ecosystem, combined with its stability and clean architecture, makes it an ideal choice for building reliable APIs. From defining endpoints to handling JSON, database connections, and HTTP methods, each part plays a crucial role in creating seamless communication between systems.
For beginners exploring java backend development, mastering REST API concepts is the perfect first step toward becoming a confident, job-ready backend developer.
Tags : .....