Spill containment is a critical requirement for laboratories, warehouses, and industrial facilities that store or handle hazardous liquids. From chemical storage rooms to manufacturing floors, effective containment systems protect employees, prevent environmental damage, and help organizations stay compliant with regulatory standards. Understanding secondary containment options, EPA requirements, and sustainable practices can help you build a safer, more responsible workplace.
What Is Secondary Containment and Why It Matters
Secondary containment is a protective system designed to capture leaks, drips, or spills from primary containers such as drums, bottles, or tanks. If the main container fails, the secondary system prevents hazardous materials from spreading into work areas, drains, or the environment.
Regulatory agencies such as the Environmental Protection Agency require secondary containment for many types of chemical storage. These requirements help reduce environmental contamination, limit worker exposure, and minimize cleanup costs. In high-risk environments, secondary containment is not just a best practice, it is an essential safety measure.
EPA-Compliant Containment Explained
EPA-compliant containment systems are designed to meet specific volume and durability standards. In general, secondary containment must be able to hold the full capacity of the largest container stored or at least ten percent of the total combined volume of all containers, whichever is greater.
To meet these standards, containment products are typically made from chemically resistant materials such as polyethylene or steel. They are engineered to withstand exposure to corrosive substances while maintaining structural integrity over time. Choosing compliant products helps facilities avoid regulatory penalties and demonstrates a commitment to safety and environmental responsibility.
Common Types of Spill Containment Solutions
There are several types of secondary containment products available, each suited to different applications and container sizes.
Drum Spill Pallets
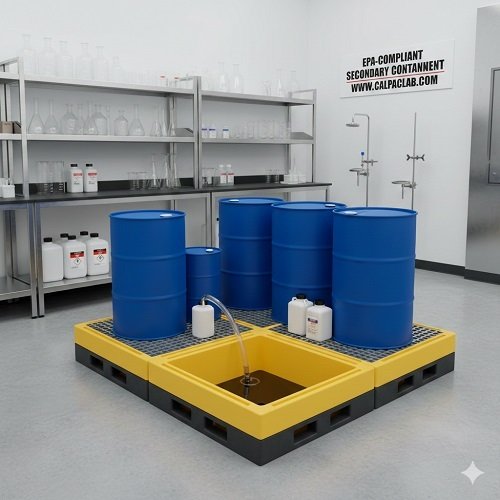
Drum spill pallets are one of the most common spill containment solutions for facilities storing large quantities of liquid chemicals. These pallets are designed to hold one or more drums while capturing leaks or spills in an integrated sump.
They are ideal for:
Storing 55-gallon drums
Managing waste collection areas
Supporting drum filling or dispensing operations
Drum spill pallets provide a stable, elevated platform while ensuring compliance with EPA secondary containment requirements.
Containment Trays
Containment trays are versatile solutions used for smaller containers, benchtop storage, or shelving units. They capture minor leaks and spills during daily handling and transfer activities.
These trays are widely used in laboratories because they are lightweight, easy to clean, and compatible with a wide range of chemicals. Containment trays are also useful for organizing Lab Supplies while maintaining a clean and safe workspace.
Secondary Storage Containers
Secondary storage containers include totes and bins designed to hold bottles, jugs, or carboys. They are commonly used in labs, chemical storage rooms, and transport applications where additional spill protection is required.
Spill Containment and Green Chemistry
Green Chemistry focuses on reducing the environmental and health impacts of chemical processes. While safer chemical alternatives help reduce risk, spills can still occur during storage or handling. That is why spill containment remains an important part of sustainable lab design.
Many modern containment products are manufactured using recyclable materials or environmentally conscious processes. Selecting durable, reusable secondary containment solutions supports Green Chemistry goals while maintaining compliance and safety.
Choosing the Right Spill Containment Solution
When selecting secondary containment products, consider the following factors:
Container size and quantity: Ensure the containment system can handle the required volume.
Chemical compatibility: Materials must resist degradation from stored substances.
Work environment: Indoor and outdoor applications may require different designs.
Ease of maintenance: Products should be easy to inspect and clean.
Regular inspections and proper employee training are also essential for maintaining an effective spill containment program.
Conclusion
Spill containment is a foundational element of laboratory and industrial safety. By implementing reliable secondary containment systems such as drum spill pallets and containment trays, organizations can meet EPA-compliant containment requirements while protecting employees and the environment.
When combined with responsible Lab Supplies management and Green Chemistry principles, effective spill containment supports safer operations, regulatory compliance, and long-term sustainability.
FAQs
What is secondary containment?
Secondary containment is a backup system that captures leaks or spills from primary containers to prevent hazardous materials from spreading.
Why is EPA-compliant containment important?
EPA-compliant containment helps facilities meet regulatory requirements, reduce environmental risk, and avoid fines or penalties.
When should drum spill pallets be used?
Drum spill pallets are recommended for storing or dispensing large drums containing hazardous or regulated liquids.
Are containment trays suitable for laboratories?
Yes, containment trays are ideal for labs because they protect work surfaces and shelves from small spills and leaks.
How does spill containment support Green Chemistry?
By preventing releases and reducing waste, spill containment complements Green Chemistry efforts focused on environmental protection and safer chemical management.