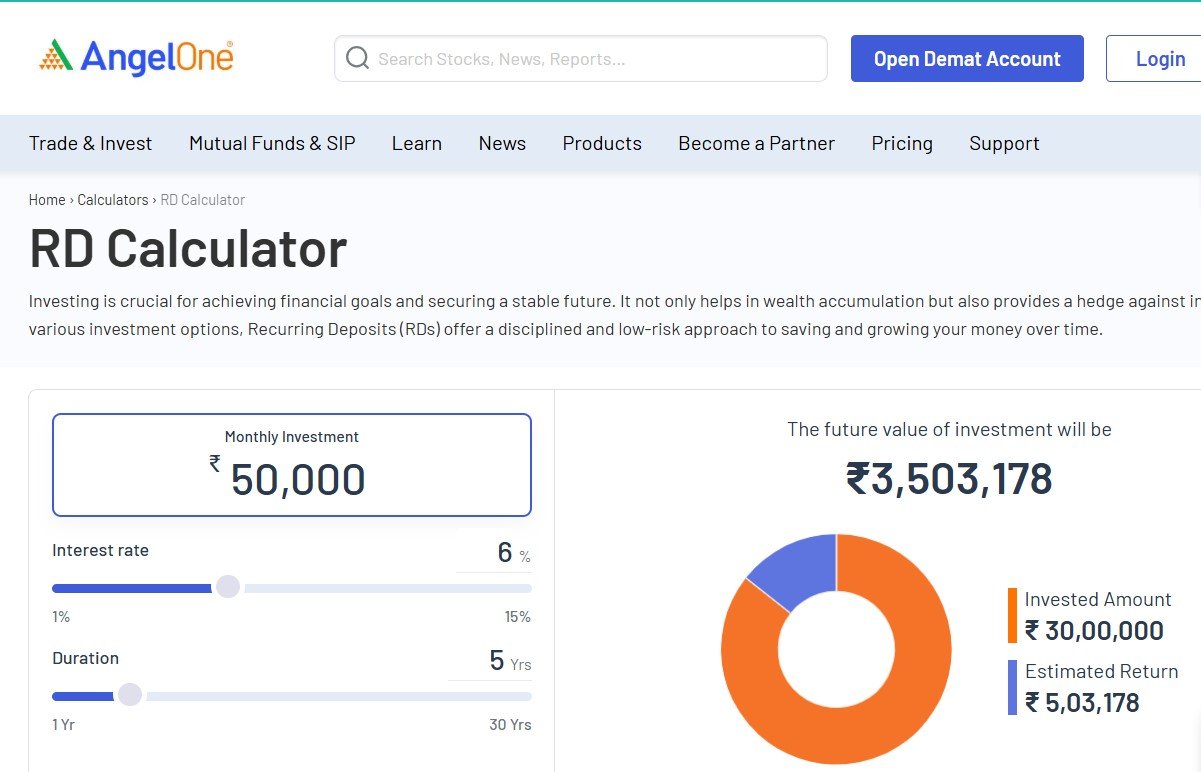
The construction industry continues to evolve as building professionals seek roofing materials that balance durability, weather resistance, and design flexibility. Traditional roofing systems, while established, often require ongoing maintenance and periodic replacement. Property owners and builders are increasingly evaluating alternatives that provide superior performance across diverse climate conditions while minimizing maintenance demands. Understanding material options and installation best practices is essential for making informed decisions about structural protection.
Understanding Composite Roofing Material Composition
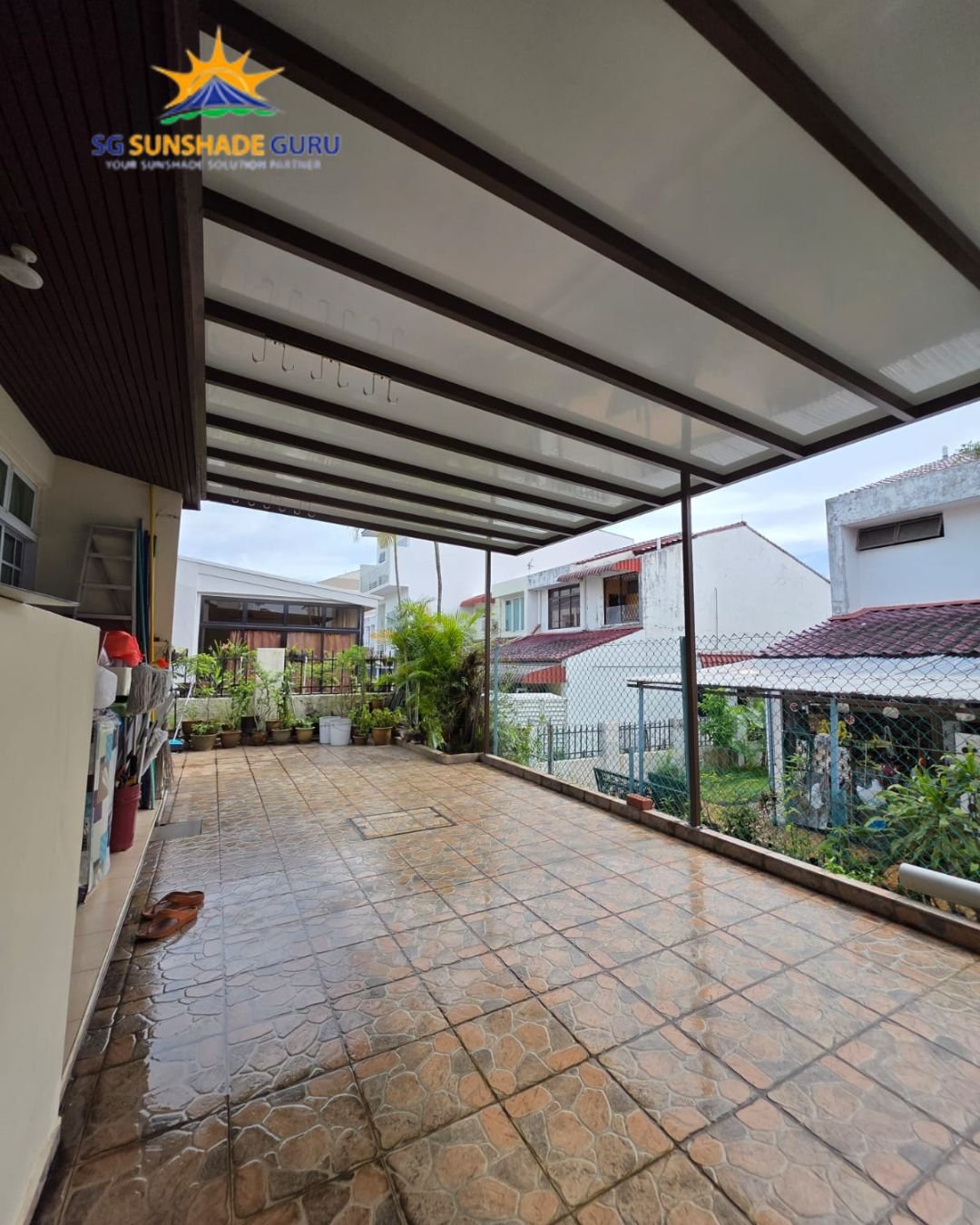
Composite roofing panels represent a significant advancement in material engineering for outdoor structures. These panels combine multiple materials—typically fiberglass, polyester, or polycarbonate bases reinforced with resin matrices—to create systems that resist UV degradation, moisture penetration, and thermal stress. The manufacturing process integrates these components into cohesive sheets that perform as unified structural elements rather than layered systems prone to separation.
The engineering behind these materials addresses common failure points found in traditional roofing. By distributing structural loads across reinforced matrices, composite panel roof systems reduce stress concentration at fastening points and seams. This distributed load capacity contributes to longevity in high-wind environments and areas experiencing significant thermal cycling between seasons.
Performance Characteristics Across Climate Conditions
Material composition directly influences how roofing systems respond to environmental exposure. Composite roofing panels demonstrate consistent dimensional stability across temperature variations, reducing the expansion and contraction cycles that stress traditional materials. In hot climates, UV-resistant resin formulations prevent surface degradation and color fading. In humid or coastal environments, the non-porous nature of composite materials prevents moisture absorption that leads to rot, mold, and structural deterioration.
Impact resistance remains a critical performance metric for roofing materials. Composite panel roof systems engineered with adequate thickness and fiber reinforcement can withstand hail, falling debris, and foot traffic without sustaining damage that compromises weatherproofing. This characteristic is particularly valuable in regions prone to severe weather events.
Installation Considerations and Long-Term Durability
Proper installation directly determines whether roofing systems deliver their designed performance levels. Fastening protocols must account for material expansion characteristics and distribute clamping forces to prevent stress concentration. Flashing details, membrane integration, and sealant compatibility require careful attention during installation planning.
Maintenance requirements differ significantly from traditional roofing systems. Composite materials do not require frequent resealing or coating applications. Periodic cleaning to remove debris and accumulated growth suffices for most installations. Inspection protocols should focus on fastener integrity and sealant condition rather than surface degradation concerns.
The structural compatibility of composite systems with existing building assemblies deserves engineering evaluation. Load-bearing capacity, connection details, and thermal bridging considerations vary based on panel thickness, profile design, and substrate specifications. Building professionals should verify that material selections align with local building codes and climatic design standards specific to project locations.
Making Informed Material Selections
Selecting appropriate roofing materials requires balancing performance expectations against installation requirements and maintenance capabilities. Composite roofing panels and composite panel roof systems offer technical advantages in specific applications, but suitability depends on climate classification, building orientation, structural load capacity, and long-term maintenance commitment.
Professional assessment by architects and structural engineers ensures that material selections align with project-specific requirements. Understanding material composition, performance characteristics, and installation best practices enables building professionals to specify systems that provide reliable structural protection and design flexibility throughout extended service life.