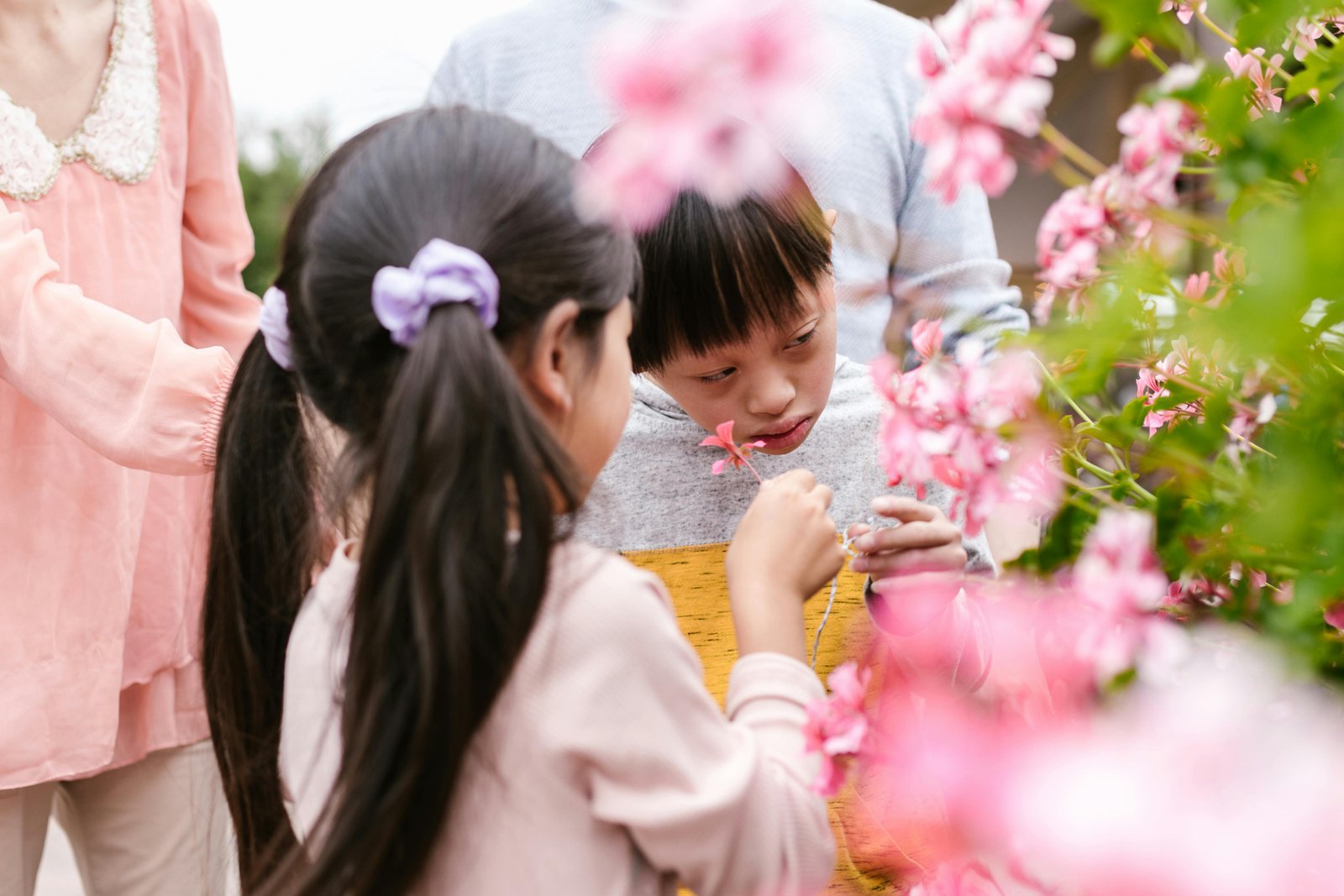
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental condition that affects how a person communicates, interacts socially, learns, and experiences the world around them. It is called a “spectrum” because autism presents differently in each individual, with a wide range of strengths, challenges, and support needs. For families, understanding autism spectrum disorder is the first step toward helping a child grow, learn, and reach their full potential.
This complete guide explains what autism spectrum disorder is, its common signs, how it is diagnosed, and the key developmental areas that support services often address.
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism spectrum disorder typically appears in early childhood, often before the age of three. It affects brain development, influencing behavior, communication, social skills, and sensory processing. Some individuals with autism may need significant support in daily life, while others may live independently with minimal assistance.
Autism spectrum disorder is not an illness or disease—it is a lifelong condition. With early identification and appropriate intervention, children with autism can make meaningful progress in communication, learning, and independence.
Common Signs and Characteristics of Autism Spectrum Disorder
Every child with autism spectrum disorder is unique, but there are common characteristics that families may notice. These signs can vary in intensity and may change as the child grows.
Social challenges may include difficulty making eye contact, limited interest in peers, or challenges understanding social cues such as facial expressions or body language.
Communication differences can range from delayed speech to difficulty starting or maintaining conversations. Some children may use few words, while others may speak fluently but struggle with back-and-forth communication.
Behavioral patterns often include repetitive movements, strong interests in specific topics, or a need for routines and predictability.
Sensory sensitivities may involve being overly sensitive or under-responsive to sounds, lights, textures, or smells.
Recognizing these early signs of autism spectrum disorder allows families to seek professional evaluation and support as soon as possible.
Causes and Risk Factors of Autism Spectrum Disorder
There is no single known cause of autism spectrum disorder. Research shows that ASD develops due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors that affect early brain development. Autism is not caused by parenting style, diet, or vaccines.
Having a family history of autism, certain genetic conditions, or complications during pregnancy may increase the likelihood of autism spectrum disorder. Ongoing research continues to improve our understanding of these factors.
Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism spectrum disorder is typically diagnosed through developmental screenings and comprehensive evaluations conducted by qualified professionals. Pediatricians, psychologists, and developmental specialists assess a child’s behavior, communication, social interaction, and developmental history.
Early diagnosis is important because it opens the door to early intervention services. The earlier support begins, the more opportunities children have to develop critical skills during key stages of brain development.
Core Developmental Areas Supported in Autism Spectrum Disorder
Support services for autism spectrum disorder focus on helping children build essential life skills across multiple developmental areas. These services are often personalized to meet the child’s specific strengths and challenges.
Social Skills Development
Children with autism spectrum disorder may find social interaction challenging. Social skill support helps children learn how to engage with peers, take turns, share, and understand social expectations. Improving social skills builds confidence and supports meaningful relationships at home, school, and in the community.
Communication Skills
Communication is a key focus area in autism spectrum disorder support. Services may address verbal language, nonverbal communication, understanding instructions, and expressing needs and emotions. Enhancing communication skills helps reduce frustration and supports independence.
Self-Help and Daily Living Skills
Self-help skills include activities such as dressing, eating, toileting, and personal hygiene. Teaching these skills empowers children with autism spectrum disorder to become more independent in daily routines and builds confidence over time.
Motor Skills Development
Motor skills include both fine motor skills (such as writing, buttoning, or using utensils) and gross motor skills (such as running, jumping, and balance). Supporting motor development helps children participate more fully in play, school activities, and everyday tasks.
Flexibility and Adaptability
Many children with autism spectrum disorder prefer routines and may struggle with change. Flexibility training focuses on helping children adapt to new situations, transitions, and unexpected changes, reducing anxiety and challenging behaviors.
Play Skills
Play is an important part of childhood development. Children with autism spectrum disorder may need support learning how to play independently, engage in imaginative play, or interact with peers during playtime. Developing play skills supports learning, creativity, and social growth.
Attention and Focus
Difficulties with attention and focus are common in autism spectrum disorder. Targeted support helps children improve their ability to concentrate, follow instructions, and complete tasks, which is especially important for success in school settings.
Behavioral and Academic Skills
Behavioral support focuses on encouraging positive behaviors and reducing behaviors that interfere with learning. Academic skill development includes early learning, reading, writing, math, and classroom readiness. Together, these supports help children succeed in educational environments.
Sensory Processing Support
Many children with autism spectrum disorder experience sensory processing challenges. Sensory support helps children better tolerate and respond to sensory input such as sounds, textures, and movement. Improving sensory regulation can lead to better attention, behavior, and emotional regulation.
The Importance of Early Intervention for Autism Spectrum Disorder
Early intervention plays a critical role in supporting children with autism spectrum disorder. Evidence-based therapies, such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), speech therapy, and occupational therapy, are commonly used to address developmental delays and build essential skills.
Early support helps children develop communication, social interaction, and adaptive skills during the most important years of brain development. Families also benefit from guidance, education, and strategies to support their child at home.
Supporting Families Living with Autism Spectrum Disorder
Raising a child with autism spectrum disorder can be both rewarding and challenging. Families often play a central role in their child’s development. Learning about autism, accessing professional support, and connecting with community resources can make a significant difference.
With the right services and consistent support, children with autism spectrum disorder can learn, grow, and thrive in their own unique ways.
Final Thoughts
Autism spectrum disorder is a complex and diverse condition that affects each individual differently. Understanding what autism spectrum disorder is and how it impacts development empowers families to make informed decisions and seek appropriate support.
By focusing on key areas such as social skills, communication, self-help, motor development, flexibility, play, attention and focus, behavioral and academic skills, and sensory processing, families can help their children build meaningful skills for lifelong success. With early intervention, compassion, and the right support, children with autism spectrum disorder can achieve their full potential.
Tags : Autism Health ABA Therapy